Future Trade conference 2022: Which way to go, e-commerce?
In May the second Future Trade conference was organised in Budapest. Participants discussed the latest trends, solutions and technologies that online retailers can use to stay in the game.

Prof. dr. Jesse Weltevreden,
Amsterdam University
The first speaker was Prof. Dr Jesse Weltevreden from the Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences, who talked about European e-commerce trends. He called attention to the high proportion of online shoppers in Europe: their penetration rate is the highest, 94% in the Netherlands and it is the lowest, 42% in Bulgaria; Hungary is at 74%. B2C e-commerce sales were the biggest in the United Kingdom in 2021, at EUR 162.3bn; in Hungary this value was EUR 2.6bn.
Difficult to remain competitive

Norbert Madar, a GKID lead consultant and partner
In his presentation Norbert Madar, lead consultant and partner of GKID called attention to the following fact: although the level of inflation is 9% on paper, in real life this rate is actually much higher. He revealed that in Hungary the average online shopper buys 19-20 times a month. Before the pandemic this number was 1 per month in the first quarter of the year. GKID’s lead consultant reckons that the most important characteristics of Hungarian e-commerce is a limited buyer base, strong regional disparities, low basket value and buying frequency, too many cash transactions, online/offline synergy, and fierce regional competition in which Hungary is lagging behind Poland, the Czech Republic, Austria and Romania.
Quality and speed
Nielsen IQ’s Katalin Séra and Gergely Kovács gave a presentation together, and the topic was this year’s market trends and expectations.


Gergely Kovács and Katalin Séra, NielsenIQ
Mr Kovács said the annual growth is driven by the drug categories, and the reason of the value sales growth is rising prices. The level of inflation is above the FMCG growth rate, which means that volume sales are shrinking in several categories. Ms Séra spoke about shoppers buying fewer times after the pandemic, while the basket value is on the rise. The latter increased by 1.3% from 2021 to 2022 and the number of transactions grew by 7.4%. In the FMCG sector the inflation rate is now bigger than 10%.
Hungary isn’t among the leaders

Dr. Ákos Kozák business futurist
Business futurist Dr Ákos Kozák told: in Hungary the last few years were about falling behind in the race with our competitors. Because of the pandemic, the size of the labour source reduced by 78,000 people. At the moment about 200,000 Hungarians don’ have a job, while employers are trying to recruit 80,000-100,000 workers. As for the short-term risks of the Hungarian economy, raw material shortage and high transportation costs hinder production the most. Retail confidence is bigger than consumer confidence. In connection with long-term risks, Dr Kozák said: according to the IMF’s GDP forecast, this year Hungary is expected to perform better than most countries in the region, but the growth is likely to slow down next year. //
Related news
KSH: The volume of exports of food, beverages and tobacco decreased by 5.7 percent, while imports decreased by 13 percent
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
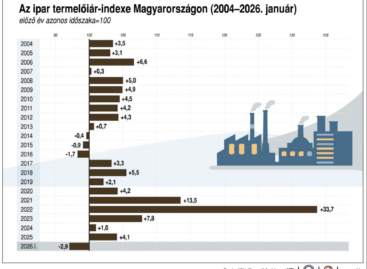
Read more >KSH: In January 2026, industrial producer prices were on average 2.9 percent lower than a year earlier and 0.9 percent higher than the previous month
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >Related news
How does the forint exchange rate affect consumer prices?
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >HELL CITY has arrived, led by Michele Morrone
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >Two million people have already voted, so 57 million forints will be given to locals in 125 settlements, courtesy of Tesco
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >