GKI Analysis: Why are food prices constantly rising?
In recent times, the rise in the prices of basic foodstuffs, especially milk and eggs, has received special attention, affecting broad segments of the population. The development of high food prices is a complex process influenced by numerous domestic and international factors. Experience from previous years shows that the effectiveness of price-influencing measures, such as price caps, may be questionable, as they result in shortages for some products, while market participants try to compensate for their lost income in other areas.
The challenges posed by high food prices were already evident in the 2022–23 period, when the temporarily introduced price stops and price caps were applied. These measures were not preceded by extensive professional and social consultation. Several professional organizations, including the MNB, have criticized previous price restrictions, as they led to supply difficulties for some products and did not prevent further increases in inflation. The trade sector compensated for the lost revenue by raising the prices of other products, which ultimately also contributed to the price increase.
Agricultural and food producer and food consumer price index, 2010=100%
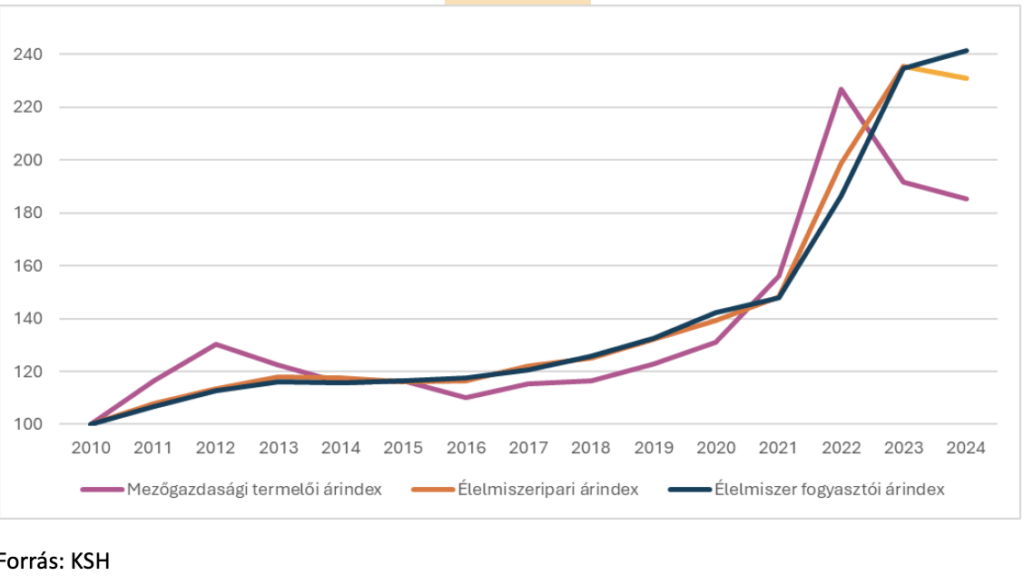
From 2010 to 2021, the examined price indices increased by 48-50%, but from 2021 to 2024, in 4 years, the food industry price index increased by almost another 56%, while the food price index increased by 63%. In other words, the food industry and consumer price indices moved strongly together, so retail chains raised their prices almost as much as they bought processed food from food companies at a higher price. The opening in 2024 is the “blessing” effect of the increase in the retail special tax, which was partly introduced by retailers on food.
Moving further back in the production chain, the situation is a little different. The producer price index, which shows how much more or less expensive Hungarian agricultural producers sell their goods for, was much more volatile than the other two. This is obviously influenced by the greater uncertainty caused by the weather, but also an important factor is the small proportion of domestic agricultural raw products in total household consumption, partly because some of the food purchased by the population comes from abroad.
What domestic influences drove the increase in food industry and food prices? The most important effects include the increase in agricultural producer prices, the surge in energy prices (domestic producers receive electricity at a price approximately 20-30% higher than their EU counterparts), the increase in official fees, the increase in the cost of packaging materials and fuels (+90%) (which was also fueled by the increase in product fees – ERP), and not least the increase in wage costs and the special retail tax imposed on large international chains that conduct the vast majority of food retail. In addition, storage has become more expensive and, due to the weaker euro exchange rate, imported food also costs more.
Related news
How does the forint exchange rate affect consumer prices?
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >The GKI business climate index rose in February
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >At K&H AI implementation is coupled with knowledge development
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >Related news
Sentix: investor sentiment in the eurozone deteriorated in March
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >Home or parcel machine? It’s been revealed how Hungarians order and what they fear most about delivery
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >Frost, cost shock, generational change: the pálinka sector is cornered on several fronts at once
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >








