The essential guide to food and agriculture
New findings indicate the food crisis in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) shows little sign of abating, and could worsen in the coming months without scaled-up assistance, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Food Programme (WFP) warned today.

Some 27 million people, one-quarter of DRC’s population, face crisis or emergency acute food insecurity conditions, fueled by poor harvests, violence-driven displacement, disease and collapsing infrastructure, according to the latest Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) analysis, which was also issued today.
The number of people in the country who fall in the IPC’s crisis phase of acute food insecurity, or IPC 3, is higher than any other country analysed by the IPC.
The new IPC report, showing even areas in and around the capital Kinshasa badly affected, forecasts the alarming hunger numbers are likely to remain unchanged through the first half of 2022. Indeed, the nutrition picture could even worsen in some regions and among particularly vulnerable groups, including young children and pregnant or nursing mothers.
“The food situation for many people in the Democratic Republic of the Congo remains desperate, with so many different obstacles – insecurity, disease, devastation and lack of infrastructure, low access to quality inputs and finance to name but a few – ganging up against their chances of being able to properly feed themselves and their families. The only way to break the cycle and shift these trends is to help them increase their resilience and productivity,” said Aristide Ongone, the FAO Representative in the DRC
“These numbers are a wake-up call for more action and to do things differently,” said WFP DRC Country Representative and Country Director, Peter Musoko. “Right now, it feels like we’re bailing out a leaky boat. We need to get together with the government, our partners and the private sector, to figure out how to give hope to the people of this country.”
The DRC’s food crisis stems from a toxic mix of factors. Agricultural production has languished amid violence and insecurity, which have cut off whole communities from their fields. Transport and communication infrastructure are crumbling. Multiple armed groups have displaced millions, especially in the Northeast, where insecurity is on the rise in two particular hotspots, despite a state of emergency imposed in May.
Even where food is available, high prices and falling incomes mean many people are unable to afford proper nutrition. While the country has experienced a complex and protracted crisis for over two decades, the devastating effects of natural disasters have also been exacerbated by the impact of COVID-19.
The pandemic and measures to contain its spread have devastated the economy, with the local currency plunging and millions losing their jobs, including in the informal sector. Agricultural livelihoods have been hard hit due to a mix of factors, from the coronavirus fallout to insecurity, which have limited farmers’ access to inputs and markets, shrunk production and decimated crops and livestock.
Related news
The value of foreign trade in pork fell at the beginning of the year
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
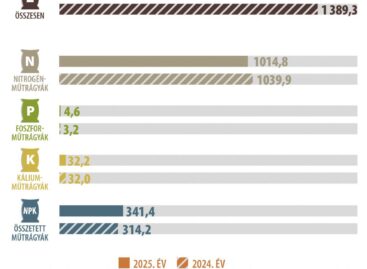
Read more >The volume of fertilizer sold did not change in 2025
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >The government strengthens the domestic agriculture with more than 1,000 billion forints of development resources
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >Related news
Eggs may be on the Easter table at last year’s price
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >Slaughter pig prices fell further: February production levels were 23.7% lower
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >Spring steps against grapevine golden yellow disease
🎧 Hallgasd a cikket: Lejátszás Szünet Folytatás Leállítás Nyelv: Auto…
Read more >